ENHANCING CALLUS FORMATION IN TAPAKTUAN PATCHOULI THROUGH IN VITRO OPTIMIZED COMBINATIONS OF PGR
Downloads
Article Highlight
- Different varieties of Patchouli exhibited different growth pattern as well as in vitro culture
- In order to induce callus, it has been determined that the combination of regulators is necessary.
- Benzylaminopurine has been identified as a potential regulator that could be used to further develop the patchouli callus of Tapak Tuan.
Abstract:
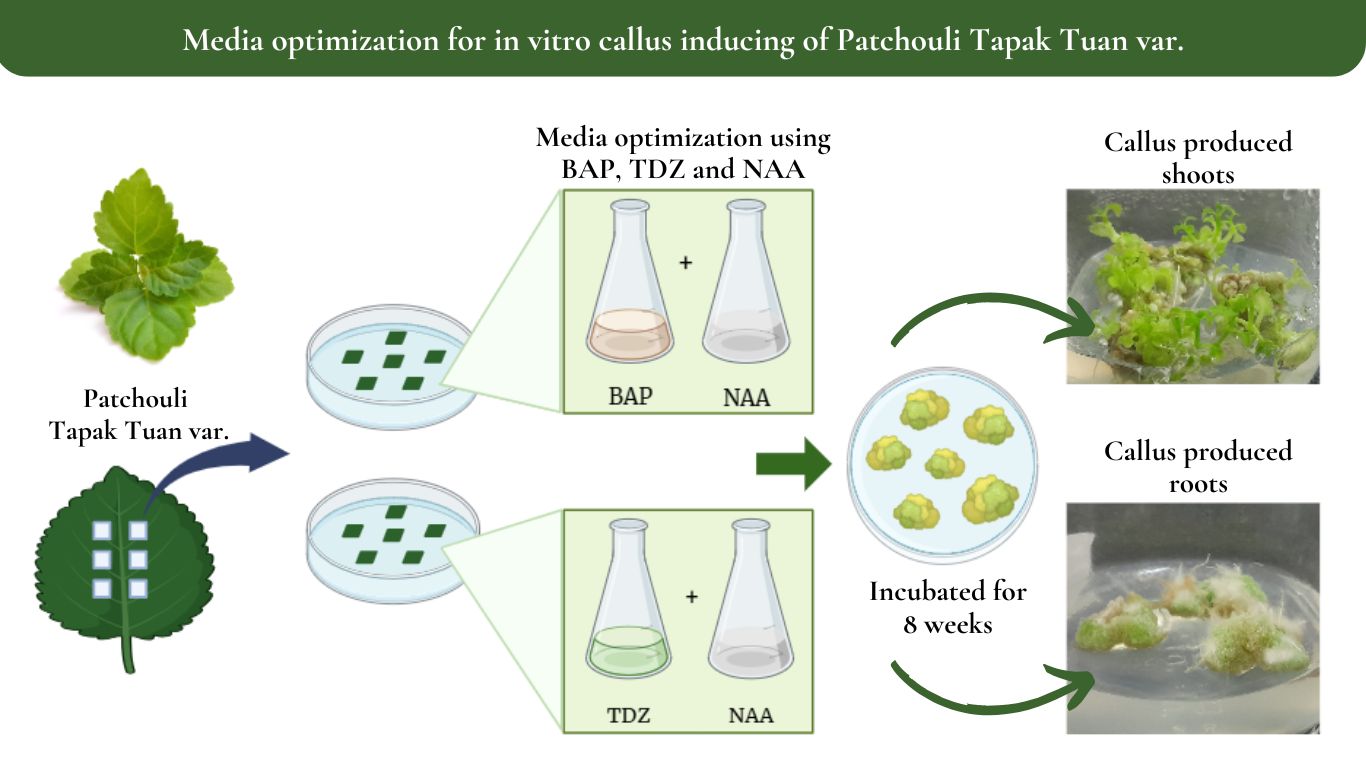
Patchouli is known for its highly demanded essential oil. The Patchouli Tapaktuan variety is the most widely cultivated by local farmers in Aceh due to its high oil yield. Currently, the study and propagation of patchouli through a biotechnological approach is being developed, one of which is in vitro culture method. In this method, suitable Plant Growth Regulators (PGR) are being observed to enhance the growth of the explant. PGRs are synthetic compounds that are added to media in plant tissue culture to stimulate plant growth. This study aimed to analyze and optimize the effect of benzylaminopurine (BAP), thidiazuron (TDZ) combined with Naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) on the growth of Tapaktuan patchouli leaf callus. This study was carried out by using a completely randomized design with seven treatments. Each treatment was replicated four times and each replicate contained three explants. The concentrations used were BAP 0.75 mg/L, TDZ 1 mg/L, and NAA in the 0.25 - 0.75 mg/L range. According to this study, combining BAP and NAA was the most effective for inducing callus in Tapaktuan patchouli leaves. The combination of BAP 0.75 mg/L + NAA 0.5 mg/L (treatment A2) was the most effective for inducing callus formation. This treatment resulted in the quickest callus development, the highest percentage of callus formation, and the largest callus diameter. Explants cultured with BAP produced a greenish-yellow callus having the potential for organogenesis culture, which could produce shoots having the ability for producing mass plantlets.
Downloads
Ali H, Khan MA, Kayani WK, Khan T, Mashwani ZR, Ullah N, Khan RS. 2018. Thidiazuron regulated growth, secondary metabolism and essential oil profiles in shoot cultures of Ajuga bracteosa. Ind Crops Prod 121(1):418-27. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.05.043 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.05.043
Anwar N, Isda MN. 2021. Respons pembentukan kalus daun pegagan (Centella asiatica (L.) Urb.) dengan penambahan naphtalene acetic acid dan benzyl amino purin secara in vitro. [Response formation of Gotu Kola leaf callus (Centella asiatica (L.) Urb.) with addition of naphtalene acetic acid and benzyl amino purine in vitro]. Biota 5(2):136-42. DOI: 10.24002/biota.v5i3.3232 DOI: https://doi.org/10.24002/biota.v5i3.3232
Bano AS, Khattak AM, Basit A, Alam M, Shah ST, Ahmad N, …, Mohamed HI. 2022. Callus induction, proliferation, enhanced secondary metabolites production and antioxidants activity of Salvia moorcroftiana L. as influenced by combinations of auxin, cytokinin and melatonin. Braz Arch Biol Technol 65(1):1-16. DOI: 10.1590/1678-4324-2022210200 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4324-2022210200
Bidabadi SS, Jain SM. 2020. Cellular, molecular, and physiological aspects of in vitro plant regeneration. Plants 9(6):702. DOI: 10.3390/plants9060702 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9060702
Deepa AV, Anju M, Thomas TD. 2018. The applications of TDZ in medicinal plant tissue culture. In: Ahmad N, Faisal M (Editors). Thidiazuron: From urea derivative to plant growth regulator. Singapore (SG): Springer Nature Singapore. p. 297-316. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-10-8004-3_15 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8004-3_15
Deswiniyanti NW, Lestari NKD. 2020. In vitro propagation of Lilium longiflorum bulbs using NAA and BAP plant growth regulator treatment. KnE Life Sci 2020:32-45.DOI: 10.18502/kls.v5i2.6437 DOI: https://doi.org/10.18502/kls.v5i2.6437
Directorate General of Estates. 2022. Statistical of National Leading Estates Crops Commodity 2020-2022. Jakarta (ID): Secretariat of Directorate General of Estates, Ministry of Agriculture of the Republic of Indonesia.
Ernawati E, Masbar R, Majid MSA, Jamal A. 2021. Production and marketing efficiency of patchouli oil industry in Indonesia. Regional Science Inquiry 13(2):135-48.
Faisal M, Ahmad N, Anis M, Alatar AA, Qahtan AA. 2018. Auxin-cytokinin synergism in vitro for producing genetically stable plants of Ruta graveolens using shoot tip meristems. Saudi J Biol Sci 25(2):273-77. DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.09.009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.09.009
Fanata WID, Qudsiyah DH. 2020. Daya regenerasi kalus dan tunas in vitro padi varietas Tarabas pada berbagai konsentrasi 2,4-D. [In vitro callus and plant regeneration rate of Tarabas rice on several concentrations of 2,4-D]. Jurnal Bioteknologi & Biosains Indonesia (JBBI) 7(2):250-8. DOI: 10.29122/jbbi.v7i2.4404 DOI: https://doi.org/10.29122/jbbi.v7i2.4404
Fehér A. 2019. Callus, dedifferentiation, totipotency, somatic embryogenesis: What these terms mean in the era of molecular plant biology? Front Plant Sci 10(4): 1–11. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00536 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00536
Fitroh AI, Dwiyani R, Wijaya IKA, Yuswanti H. 2018. Pengaruh 2,4-D terhadap induksi kalus daun stroberi (Fragaria sp.) dengan media alternatif nutrisi hidroponik AB mix [Influence of 2,4-D to induce callus from strawberry leaves (Fragaria sp.) on alternative media of AB mix hydroponic nutrient]. AgroTrop 7(3):304-15.
Florenika N, Wijaya AN, Restanto DP, Hardjo PH. 2022. Regeneration of Pogostemon cablin Benth. ‘'Sidikalang’ through indirect organogenesis and shoot multiplication for production of true-to-type plant. Agriprima 6(1):1–11. DOI: 10.25047/agriprima.v4i2.375 DOI: https://doi.org/10.25047/agriprima.v6i1.447
Gharari Z, Bagheri K, Karimkhanlooei G, Sharafi A. 2021. Study of tissue culture and in vitro organogenesis of Scutellaria bornmuelleri using benzylaminopurine, isopentenyl adenine and thidiazuron. S Afr.J Bot 139:458-69. DOI: 10.1016/j.sajb.2021.03.030 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2021.03.030
Gopi C. 2017. High frequency of plant regeneration through adventitious shoots proliferation from leaf explant of patchouli Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth. Int J Curr Res Biosci Plant Biol 4(7):134-9. DOI: 10.20546/ijcrbp.2017.407.017 DOI: https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcrbp.2017.407.017
Habibah NA, Safitri S, Pratiwi YR, Wijawati N, Musafa F, Puspitasari ADS, Yuniastuti A. 2021. Callus induction from tuber of lesser yam (Dioscorea esculenta) on MS media supplemented by 2,4-D and kinetin. J Phys: Conf Ser 1918(2021):052029. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/1918/5/052029 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1918/5/052029
Hemmati, N., Cheniany, M., Ganjeali, A. 2020. Effect of plant growth regulators and explants on callus induction and study of antioxidant potentials and phenolic metabolites in Salvia tebesana Bunge. Bot Serb 44(2):163-73. DOI: 10.2298/BOTSERB2002163H DOI: https://doi.org/10.2298/BOTSERB2002163H
Jafari A, Kahrizi D, Mansouri M. 2016. Effects of plant growth regulators and explant on callus induction in pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium L.). Biharean Biol 10(2):134-6.
Kandarihi O, Muddarisna N, Prasetyo IK. 2015. Pengaruh konsentrasi dan berbagai macam substansi pengatur tumbuh terhadap pertumbuhan awal stek tanaman nilam (Pogostemon cablin Benth) varietas Sidikalang. [Effect of concentration and various growth regulator substances on the initial growth of patchouli (Pogostemon cablin Benth) Sidikalang variety cuttings]. Primordia 10(2):18-29.
Kawochar MA, Ahmed NU, Hossain MI, Ferdous J. 2017. Role of explants and NAA on callus Induction of potato (Solanum tuberosum). Am.J.Life Sci 5(5):140-4. DOI: 10.11648/j.ajls.20170505.14 DOI: https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajls.20170505.14
Korasick DA, Enders TA, Strader LC. 2013. Auxin biosynthesis and storage forms. J Exp Bot 64(9):2541-55. DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ert080 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert080
Kotov AA, Kotova LM. 2023. Auxin/cytokinin antagonism in shoot development: From moss to seed plants. J Exp Bot 74(21):6391-5. DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erad417 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erad417
Kurepa J, Smalle JA. 2022. Auxin/cytokinin antagonistic control of the shoot/root growth ratio and its relevance for adaptation to drought and nutrient deficiency stresses. Int J Mol Sci 23(4):1933. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23041933 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23041933
Lalthafamkimi L, Bhau BS, Kumar S, Mukhia S, Kumar R, Banik D, Bhattacharyya P. 2022. Indirect organogenesis mediated high frequency conversion of non-embryonic synthetic seeds, essential oil profiling and antibacterial activity in genetically stable plants of Patchouli. Biotech 12(12):349. DOI: 10.1007/s13205-022-03302-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03302-3
Munsell AH. 1977. Munsell Color Charts for Plant Tissues: 2nd Edition, revision. Baltimore (US): Munsell Color.
Nazir M, Ullah MA, Younas M, Siddiquah A, Shah M, Giglioli-Guivarc’h N, …, Abbasi BH. 2020. Light-mediated biosynthesis of phenylpropanoid metabolites and antioxidant potential in callus cultures of purple basil (Ocimum basilicum L. var purpurascens). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 142(2020:107-20. DOI: 10.1007/s11240-020-01844-z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01844-z
Pulianmackal AJ, Kareem AVK, Durgaprasad K, Trivedi ZB, Prasad K. 2014. Competence and regulatory interactions during regeneration in plants. Front Plant Sci 5:142. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00142 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00142
Puspita DE, Efendi E, Zakaria S, Sriwati R. 2023. Indirect organogenesis of Aceh patchouli leaf explants (Pogostemon cablin Benth ) by in vitro. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 1183(2023):012052. DOI: 10.1088/1755-1315/1183/1/012052 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1183/1/012052
Rahayu T, Mardini U. 2015. Respon eksplan nodus dan daun tanaman Binahong (Anredera cordifolia L.) pada media MS dengan variasi konsentrasi BAP [The response of node and leaf explant of binahong (Anredera cordifolia L.) on MS media with variation of BAP concentration]. Proceeding Biology Education Conference 12(1):657-61.
Rahmawati M, Safira CN, Hayati M. 2021. Perbanyakan tanaman nilam Aceh (Pogostemon cablin Benth.) dengan kombinasi IAA dan kinetin secara in vitro [Propagation of Aceh patchouli (Pogostemon cablin Benth.) with a combination of IAA and kinetin in vitro]. Agrium 18(1):25-33. DOI: 10.29103/agrium.v18i1.3839 DOI: https://doi.org/10.29103/agrium.v18i1.3839
Rasud Y, Bustaman B. 2020. Induksi kalus secara in vitro dari daun cengkeh (Syzigium aromaticum L.) dalam media dengan berbagai konsentrasi auksin [In vitro callus induction from clove (Syzigium aromaticum L.) leaves on medium containing various auxin concentrations]. Jurnal Ilmu Pertanian Indonesia (JIPI) 25(1):67-72. DOI: 10.18343/jipi.25.1.67 DOI: https://doi.org/10.18343/jipi.25.1.67
Restanto DP, Farlisa VY, Dewanti P, Hariyono K, Handoyo T. 2022. Induksi somatic embriogenesis dan kultur suspensi sel pada tanaman porang (Amorphophallus muelleri Blume). [Induction of somatic embryogenesis and cell suspension culture in porang plants (Amorphophallus muelleri Blume)]. Agriprima 6(2):111-23. DOI: 10.25047/agriprima.v6i2.448 DOI: https://doi.org/10.25047/agriprima.v6i2.448
Sagharyan M, Ganjeali A, Cheniany M, Kouhi SMM. 2020. Optimization of callus induction with enhancing production of phenolic compounds production and antioxidants activity in callus cultures of Nepeta binaloudensis jamzad (Lamiaceae). Iran J Biotechnol 18(4):47-55. DOI: 10.30498/IJB.2020.2621
Septiana AA. 2014. Pengaruh hormon IAA dan BAP terhadap perbanyakan tanaman kentang (Solanum tuberosum L.) secara in vitro [Effect of IAA and BAP hormones on potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) plant propagation in vitro]. [Undergraduate Thesis]. Jember (ID): Faculty of Agriculture, Universitas Jember.
Silalahi M. 2015. Pengaruh modifikasi media Murashige-Skoog (MS) dan zat pengatur tumbuh BAP terhadap pertumbuhan kalus Centella asiatica L. (urban) [Effect of modified Murashige-Skoog (MS) medium and growth regulator BAP on callus growth of Centella asiatica L. (urban)]. Pro-Life 2(1):14-23.
Sosnowski J, Truba M, Vasileva V. 2023. The impact of auxin and cytokinin on the growth and development of selected crops. Agriculture 13(3):724. DOI: 10.3390/agriculture13030724 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030724
Su YH, Liu YB, Zhang XS. 2011. Auxin-cytokinin interaction regulates meristem development. Mol Plant 4(4):616-25. DOI: 10.1093/mp/ssr007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr007
Sudrajad H, Wijaya NR. 2019. Pengaruh kinetin dan NAA terhadap induksi kalus Pule Pandak (Rauvolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. ex Kurz) [The effect of kinetin and NAA on callus induction of Indian snakeroot (Rauvolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. ex Kurz).]. Jurnal Tumbuhan Obat Indonesia 12(2):68-74. DOI: 10.22435/jtoi.v12i2.1691 DOI: https://doi.org/10.22435/jtoi.v12i2.1691
Swamy MK, Sinniah UR. 2016. Patchouli (Pogostemon cablin Benth.): Botany, agrotechnology and biotechnological aspects. Ind Crops Prod 87:161-76. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.032 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.032
Taghizadeh M, Nasibi F, Kalantari KM, Benakashani F. 2020. Callogenesis optimization and cell suspension culture establishment of Dracocephalum polychaetum Bornm. and Dracocephalum kotschyi Boiss.: An in vitro approach for secondary metabolite production. S Afr J Bot 132:79-86. DOI: 10.1016/j.sajb.2020.04.015 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2020.04.015
Tarigan SDS, Astarini IA, Astiti NPA. 2023. Inisiasi kalus bangle (Zingiber purpureum Roscoe) pada beberapa kombinasi 2,4-D dan kinetin [Callus initiation of casumunar ginger (Zingiber purpureum Roscoe) on several combinations of 2,4-D and kinetin]. Jurnal Hortikultura Indonesia (JHI) 14(2):93-9. DOI: 10.29244/jhi.14.2.93-99 DOI: https://doi.org/10.29244/jhi.14.2.93-99
Tarigholizadeh S, Motafakkerazad R, Kosari-Nasab M, Movafeghi A, Mohammadi S, Sabzi M, Talebpour AH. 2021. Influence of plant growth regulators and salicylic acid on the production of some secondary metabolites in callus and cell suspension culture of Satureja sahendica Bornm. Acta Agric Slov 117(4):1-12. DOI: 10.14720/aas.2021.117.4.773 DOI: https://doi.org/10.14720/aas.2021.117.4.773
Thomy Z. 2012. Effect of plant growth regulator 2,4-D and BAP on callus growth of plants producing gaharu (Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk.). In: Situmorang M, Syamsuardi, Mulya MB, Jatmilah, Widhiastuti R, Tanjung M, Nurcahya K (Editors). Prosiding Seminar Nasional Biologi, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, 11 Mei 2012. p. 197-204.
Waryastuti DE, Setyobudi L, Wardiyati T. 2017. Pengaruh tingkat konsentrasi 2,4-D dan BAP pada media MS terhadap induksi kalus embriogenik temulawak (Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb.) [Effect of 2,4-D and BAP concentration levels in MS media on the induction of embryogenic callus of Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb.)]. Jurnal Produksi Tanaman 5(1):140-9.
Wijaya BE, Dwiyani R, Mayadewi NNA. 2023. Induksi dan multiplikasi kalus Eucalyptus sp. pada berbagai media callus induction medium (CIM) secara in vitro [Callus induction and multiplication of Eucalyptus sp. on various callus induction medium (CIM) in vitro]. Agrotrop 13(1):76-84. DOI: 10.24843/AJoAS.2023.v13.i01.p07 DOI: https://doi.org/10.24843/AJoAS.2023.v13.i01.p07
Wulandari M., Abdullah, Netty. 2022. Ketahanan kalus embrio kedelai (Glycine max L) terhadap tekanan salinitas (NaCl) secara in vitro. [Resistance of soybean (Glycine max L.) embryo callus to salinity stress (NaCl) in vitro]. Journal Techno-Eco-Farming (JTEF) 2(1):8-21. DOI: https://doi.org/10.33096/agrotekmas.v1i3.113
Zhang DJ, Yang YJ, Liu CY, Zhang F, Wu QS. 2018. Root hair growth and development in response to nutrients and phytohormones. In: Giri B., Prasad R., Varma A (Editors). Root Biology. Cham (CH): Springer International Publishing. p. 65-84. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-75910-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75910-4_3
Copyright (c) 2025 Essy Harnelly

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree with the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication, with the work 1 year after publication simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons attribution-noncommerical-noderivates 4.0 International License that allows others to share, copy and redistribute the work in any medium or format, but only where the use is for non-commercial purposes and an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal is mentioned.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).