TREE SPECIES DIVERSITY IN PHRA THAT SI MUEANG PONG AREA, CHIANG MAI PROVINCE, THAILAND
Article Highlights
- Rich tree diversity found in Phra That Si Mueang Pong area.
- Endangered species identified, promoting conservation efforts.
- Unique plant distribution influenced by land use and water proximity.
- Potential for ecotourism and environmental education in the region.
- Study provides foundational data for future ecological research.
Abstract
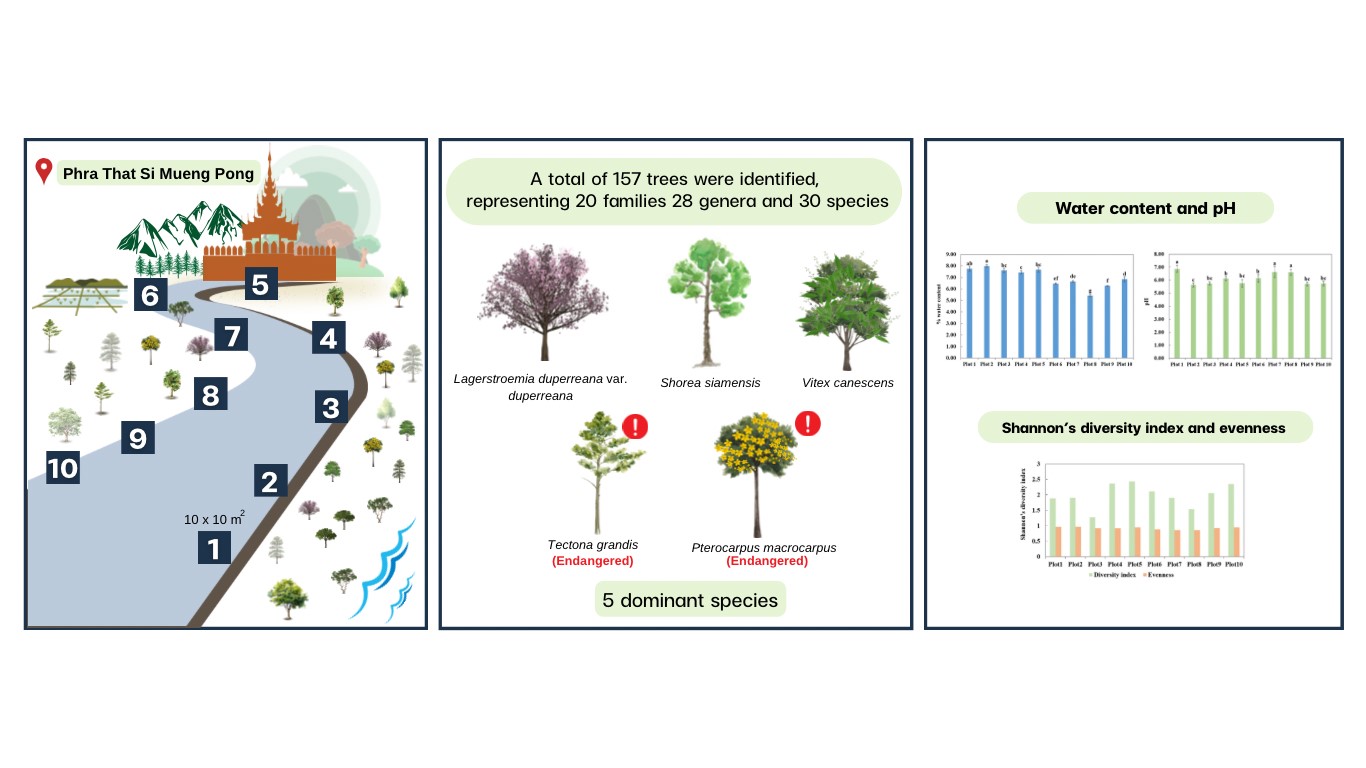
This research conducted a survey of perennial flora in ten subplots along the pathway leading to Phra That Si Mueang Pong, identifying a total of 30 species representing 20 families, 28 genera. Dominant species included Lagerstroemia duperreana var. duperreana, Shorea siamensis, Pterocarpus macrocarpus, Tectona grandis, and Vitex canescens. Families with the highest species number were Fabaceae, Lamiaceae, Combretaceae, and Malvaceae. The study revealed the presence of both common and rare plant species in the area, with differences in species distribution between plots 1-5 and 6-10. Plots 6-10, near the Mae Tha Chang River, displayed higher biodiversity, correlating with the biodiversity index. The dominant species, based on the importance value index (IVI), were Pterocarpus macrocarpus, Lagerstroemia duperreana, Tectona grandis, Shorea siamensis, and Millettia brandisiana, respectively. Two species, Pterocarpus macrocarpus and Tectona grandis, were classified as endangered. The soil analysis indicated slightly acidic pH and relatively low moisture content, with significant differences between plots 1-5 and 6-10. The study suggests the potential for ecotourism and environmental learning centers in the Chiang Mai province cultural tourism destination, emphasizing the rich biodiversity and ecological value of the mixed deciduous and dry dipterocarp forest ecosystems.
Downloads
INTRODUCTION
Exploration of biological diversity and utilization of plant resources in Thailand has been an ongoing effort, encompassing both areas of base surveys and specific group-focused investigations(Sudchaleaw et al., 2023);(Boonma et al., 2023);(Panyadee et al., 2023);(Ragsasilp et al., 2022);(Pansumrit et al., 2022);(Sutjaritjai et al., 2022);(Saensouk et al., 2021). This research unveiled that biological diversity of plant species, varying across different regions, consistently generates new knowledge and insights. While studies on plant diversity in ecotourism areas in Thailand have provided limited information, most research has focused on national parks, such as Doi Inthanon National Park, Phu Kradueng National Park, Khao Yai National Park, and Kaeng Krachan National Park.
Chiang Mai Province, located in the northern region of Thailand, has a tropical monsoon climate. The average temperature ranges from 22.3oC to 34.4oC, with annual rainfall of 972.1 mm(Center, 2020). With its mountainous terrain, there are many cultural tourist attractions situated on various mountains outside the boundaries of national parks. With a well-preserved environmental system, these factors make it feasible to promote sustainable ecotourism destinations in the future, facilitating easier access for visitors.
Phra That Si Mueang Pong, also known as the White Pagoda, stands as a prominent cultural and ecological tourist destination within the province of Chiang Mai. It is situated on the summit within the Aranyawat Temple in Hang Dong District, Chiang Mai, Thailand.
There are two routes to reach Phra That Si Mueang Pong, i.e., one involves climbing the stairs, while the other allows for driving up the road. The ascent via the staircase serves as an ecotourism route, winding through mixed deciduous forest and dry dipterocarp forest. During the climb to Phra That Si Mueang Pong, both sides of the staircase are influenced by significant factors contributing to plant diversity. One side is situated near the Mae Tha Chang River, while the other side borders an agricultural area, resulting in distinct variations in plant diversity.
Therefore, this study investigated the diversity of tree species along the ascent to Phra That Si Mueang Pong in the ecotourism area, encompassing detailed analyses of biodiversity index and importance value index. The findings from this study were expected to benefit the local community, tourists, as well as educational institutions in the vicinity to utilize the area for studying ecotourism, focusing on the diversity of tree species. Additionally, this research provided foundational information for future studies in various research areas.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Area
The study area was located surrounding Phra That Si Mueang Pong in Hang Dong District, Chiang Mai, Thailand. The geographical features comprised a mountainous terrain consisting of deciduous forest and dry dipterocarp forest, with elevations ranging from 350 to 450 meters above sea level (masl).
Data Collection
Plant diversity data were collected from 2019 to 2020 within a permanent sample plot measuring 200 x 200 m2. The quadrat method, specifically employing 10 x 10 m2subplots, was utilized for the systematic sampling of plant species. Along the ascent to Phra That Si Mueang Pong, a total of ten subplots were established, with five plots positioned on the side adjacent to the agricultural area, while the remaining five plots were situated on the side bordering the Mae Tha Chang River (Figure 1).
In each subplot, the circumference of tree trunks with a diameter greater than or equal to 15 cm was measured at a height of 1.30 m. Subsequently, the measured trees were tagged with number tapes, which also included information on the species, such as local name, common name, scientific name, and family of the perennial tree. Data on tree species were gathered through consultation with experts and relevant literature(Chayamarit & Chamchumroon, 2016). Additionally, the status of trees was assessed based on the IUCN red list of threatened species(Source Title, 2024).
Physical and chemical parameters of the soil were analyzed, including soil pH content and water content. Soil pH was determined using the Soil-H2O system(F.A.O., 2021), while soil water content was calculated as a percentage based on oven-dried soil weight according to FAO (2023) as follows:
W% =\( \documentclass{article} \usepackage{amsmath} \begin{document} \displaystyle \text{\ \ \ }\frac{M_{\text{cms}} - \ M_{\text{cds}}}{M_{\text{cds}} - M_{c}}\ \times 100 \end{document} \)\( \documentclass{article} \usepackage{amsmath} \begin{document} \displaystyle \text{\ \ \ }\frac{M_{\text{cms}} - \ M_{\text{cds}}}{M_{\text{cds}} - M_{c}}\ \times 100 \end{document} \)
where:
W = soil water content expressed in units of percentage (%)
Mcms= mass of container and moist soil (g)
Mcds= mass of container and oven dry sample (g)
Mc= mass of container (g)
Data Analysis
Data obtained from the field survey were analyzed to determine the Importance Value Index (IVI). This calculation involved assessing the Relative Density (RD), Relative Frequency (RF), and Relative Dominance (RDo), following the methodology outlined by Ismail et al. (2017). In addition, species diversity index (H’) and evenness value (E) of tree species were determined and calculated following the Shannon’s Diversity Index(Odum & Barrett, 2004).
The baseline statistics used were the mean±standard deviation. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software program. To further analyze the results, Duncan’s new multiple tests was performed at a significant level of 5%.
Figure 1.Aerial photograph of Phra That Si Mueang Pong (a) and the
Boonma T, Saensouk S, Saensouk P. 2023. Diversity and traditional utilization of the Zingiberaceae plants in Nakhon Nayok Province, Central Thailand. Diversity 15(8):904. DOI: 10.3390/d15 080904 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/d15080904
Chayamarit K, Chamchumroon V. 2016. Plant Identification Handbook. Department of National Parks, Wildlife and Plant Conservation. Bangkok (TH): Sittichoke Printing.
Chernkhunthod C, Hioki Y. 2020. Floristic composition and forest structure in different fire frequency of mixed deciduous forest, Doi Suthep-Pui National Park, Northern Thailand. J Jpn Soc Reveget Tech 46(2):202-17. DOI: 10.7211/jjsrt.46.202 DOI: https://doi.org/10.7211/jjsrt.46.202
FAO [Food and Agriculture Organization]. 2021. Standard operating procedure for soil pH determination. Rome (IT): Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
FAO [Food and Agriculture Organization]. 2023. Standard operating procedure for soil moisture content by gravimetric method. Rome (IT): Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Hanpattanakit P, Chidthaisong A. 2012. Litter production and decomposition in dry dipterocarp forest and their responses to climatic factors. GMSARN Int J 6:169-74.
IUCN [International Union for Conservation of Nature]. 2024. IUCN Red list of threatened species. Available from: https://www.iucnredlist.org. (Accessed: December 1, 2023)
Ismail MH, Zaki PH, Fuad MFA, Jemali NJN. 2017. Analysis of importance value index of unlogged and logged peat swamp forest in Nenasi Forest Reserve, Peninsular Malaysia. Bonorowo Wetl 7(2):74-8. DOI:10.13057/bonorowo/w070203 DOI: https://doi.org/10.13057/bonorowo/w070203
Makan A. 2022. Humus and humic substances: Recent advances. IntechOpen. DOI:10.5772/intechopen.100876 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.100876
Northern Meteorological Center. 2020. Report on the maximum and minimum temperatures and rainfall from the Chiang Mai weather station. Chiang Mai, Thailand. Available from: www.cmmet.tmd.go.th
Odum EP, Barrett GW. 2004. Fundamental of Ecology. 5th Edition. Philadelphia (US): W.B. Saunders.
Pansumrit P, Pathomwichaiwat T, Kladwong P, Tiyaworanant S, Nguanchoo V, Bongcheewin B. 2022. An ethnobotanical study of the genus Smilax in Thailand and its botanical authentication for Hua-khao-yen crude drugs. Pharm Sci Asia 3:230-41. DOI:10.29090/psa.2022.03. 21.220 DOI: https://doi.org/10.29090/psa.2022.03.21.220
Panyadee P, Wangpakapattanawong P, Inta A, Balslev H. 2023. Very High food plant diversity among ethnic groups in Northern Thailand. Diversity 15:120. DOI:10.3390/d15010120 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010120
Ragsasilp A, Saensouk P, Saensouk S. 2022. Ginger family from Bueng Kan Province, Thailand: Diversity, conservation status, and traditional uses. Biodiversitas 23(5):2739-52. DOI:10.13057/ biodiv/d230556 DOI: https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d230556
Rundel P, Boonpragob K., Patterson M. 2017. Seasonal water relations and leaf temperature in a deciduous dipterocarp forest in northeastern Thailand. Forest 8(10):368. DOI:10.3390/f8100368 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/f8100368
Saensouk S, Phatlamphu N, Saensouk P, Junsongduang A. 2021. Ethnobotany of edible plants in Muang District, Kalasin Province, Thailand. Biodiversitas 22(12):5432-44. DOI:10.13057/ biodiv/d221226 DOI: https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d221226
Sudchaleaw S, Saensouk S, Saensouk P, Sungkaew S. 2023. Species diversity and traditional utilization of bamboos (Poaceae) on the Phu Thai Ethnic Group in Northeastern Thailand. Biodiversitas 24(4):2261-71. DOI: 10.13057/biodiv/d240439 DOI: https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d240439
Sutjaritjai N, Panyadee P, Phumthum M, Inta A, Balslev H. 2022. High diversity of medicinal uses of Thai legumes (Fabaceae) and their potential in public herbal medicine. Diversity 14:588.DOI:10.3390/d14080588 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/d14080588
Copyright (c) 2024 Pongpan Leelahakriengkrai

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree with the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication, with the work 1 year after publication simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons attribution-noncommerical-noderivates 4.0 International License that allows others to share, copy and redistribute the work in any medium or format, but only where the use is for non-commercial purposes and an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal is mentioned.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).